What types of diodes does Toshiba provide?
There are many types of diodes. Diodes can be categorized into pn junction diodes and metal-semiconductor junction diodes known as Schottky barrier diodes (SBDs) according to their structures. Toshiba classifies diodes as follows.
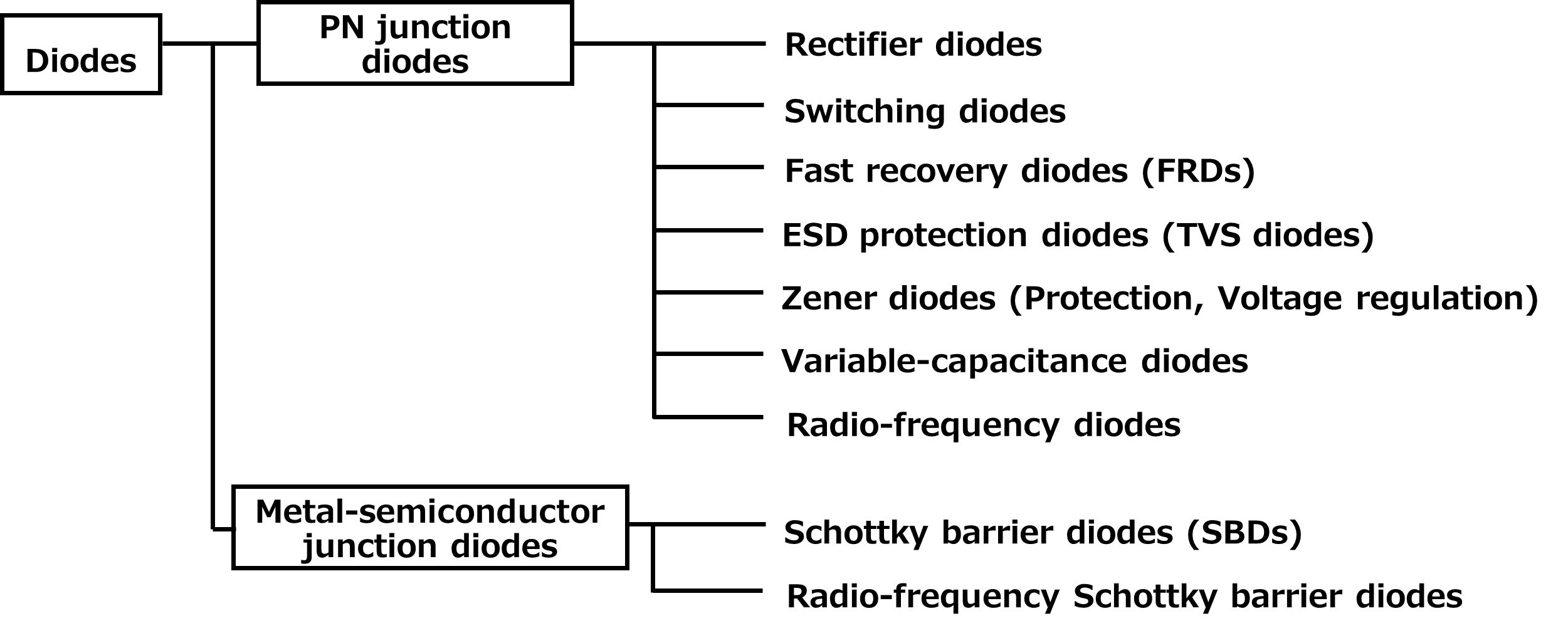
Pn junction diodes are further divided into rectifier and switching diodes that are normally used in the forward direction and Zener (constant-voltage) and ESD protection (TVS) diodes designed to exploit breakdown voltage in the reverse direction.
In addition, pn junction diodes are further subdivided by matching their processes depending on the application. For example, pn junction diodes are available in such types as: fast recovery diodes (FRDs) in which reverse recovery charge is reduced to achieve a shorter reverse recovery time than for typical rectifier diodes; variable-capacitance (varicap) diodes that utilizes the fact that the capacitance of the depletion layer changes with the reverse bias voltage; and radio-frequency switching diodes (known as PIN diodes) that have an undoped intrinsic (I) semiconductor region between p-type and n-type semiconductors to increase the width of the depletion region and thereby reduce capacitance.
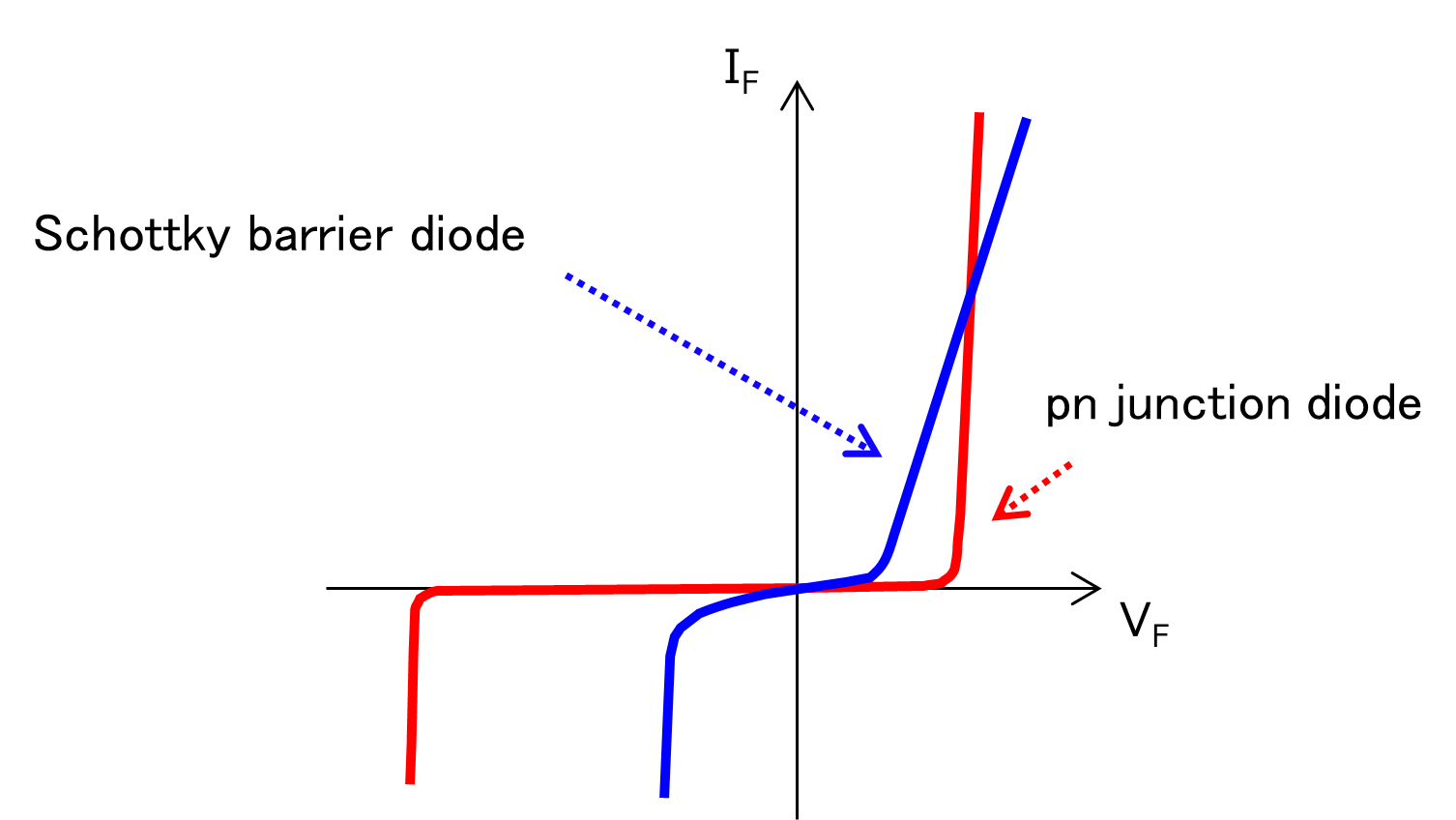
SBDs have a low forward voltage (VF), and since they are unipolar devices, they are essentially free of reverse recovery charge.
Related Links
For products, please refer to the following links.