- General Top View
-
SEMICONDUCTOR View
-
ApplicationsAutomotive
Body Electronics
xEV
In-Vehicle Infotainment
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Chassis
IndustrialInfrastructure
BEMS/HEMS
Factory Automation
Commercial Equipment
Consumer/PersonalIoT Equipment
Healthcare
Wearable Device
Mobile
Computer Peripherals
-
Products
Products
-
Design & Development
-
Knowledge
Knowledge
- Where To Buy View
-
- STORAGE View
- COMPANY View
- Part Number Search
- Cross Reference Search
- Keyword Search
- Parametric Search
- Stock Check & Purchase
This webpage doesn't work with Internet Explorer. Please use the latest version of Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox or Safari.
require 3 characters or more.
The information presented in this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's selection criteria and should be treated as a suggestion only. Please carefully review the latest versions of all relevant information on the TOSHIBA products, including without limitation data sheets and validate all operating parameters of the TOSHIBA products to ensure that the suggested TOSHIBA products are truly compatible with your design and application.
Please note that this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's estimate of compatibility with other manufacturers' products, based on other manufacturers' published data, at the time the data was collected.
TOSHIBA is not responsible for any incorrect or incomplete information. Information is subject to change at any time without notice.
require 3 characters or more.
USB (Universal Serial Bus)
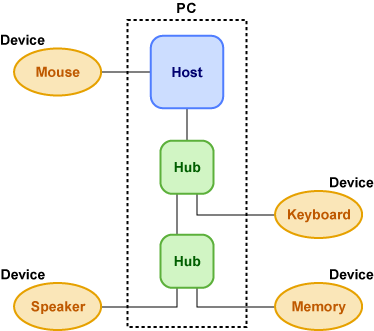
USB is a very popular serial interface especially for PCs. As well known, the interface is used to connect to a PC such equipments as a keyboard, a mouse, a printer, a Flash memory, a hard disk drive, a speaker, and so on.
USB has several speed versions, Low-Speed (1.5Mbps), Full-Speed (12Mbps), High-Speed (480Mbps) and so on.Toshiba TX03 series microprocessors support USB Full-Speed. A hierarchical structure is applied to USB interface. One “Host” dominates many “Devices” in a network. For example, a PC is a Host, and Devices are any apparatuses which are connected to the PC through USB cables, like a keyboard, a mouse and so on.
USB has a remarkable feature of plug-and-play. Switching off a PC is unnecessary when USB Devices are connected or removed. This is one of the reasons USB has become so popular.
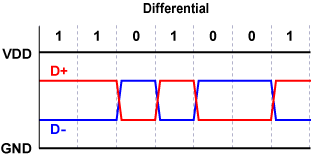
The cable of USB has 4 wires; VDD, GND, signal D+, and signal D-. D+ and D- are complementary values each other for one transferred data. In the case that D+ is high and D- is low, the data is called “Differential 1”. And D+ is low and D- is high, “Differential 0”.The data format of USB is NRZI (non-return to zero inverted). This format defines data “1” when no change occurs in one clock interval, and data “0”, either high-to-low or low-to-high change occurs.
USB does not have any clock lines. So the Host and the Driver have to synchronize each other. 8 bit SYNC codes are transferred to synchronize a receiver to a transmitter in USB Full-Speed.
Lineup
Microcontrollers products incorporating a USB interface are displayed.
Queries about purchasing, sampling and IC reliability
Stock Check & Purchase
require 3 characters or more.
| Part Number | Authorized Distributor | Stock Quantity | Date | Shopping Cart |
|---|
Through this website you are able to proceed to the website of our distributors ("Third Party Website") which is not under the control of Toshiba Corporation and its subsidiaries and affiliates (collectively "Toshiba"). The Third Party Website is made available to you as a convenience only and you agree to use the Third Party Website at your own risk. The link of the Third Party Website does not necessarily imply a recommendation or an endorsement by Toshiba of the Third Party Website. Please be aware that Toshiba is not responsible for any transaction done through the Third Party Website, and such transactions shall be subject to terms and conditions which may be provided in the Third Party Website.

