CAN (Controller Area Network)
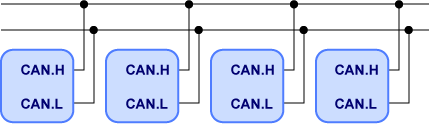
CAN is a serial interface which is mainly used inside a motor vehicle. Strong noise-immunity is realized with its double signal lines. CAN does not have any clock lines, which means it is an asynchronous interface. Only two signal lines configure the whole network.
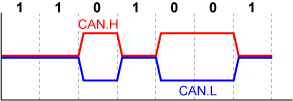
The voltage difference between the double signals, CAN.H and CAN.L, represents the data. “CAN.H-high and CAN.L-low” is assigned to data “0”, and “CAN.H = CAN.L”, data “1”. Noises will be cancelled because the transferred data is determined by the voltage difference of the pair of complementary signals.
A data transmitter and its receiver in CAN need to synchronize each other without any clock signals. Once a transmitter sends the first “0” as a start bit, the other all receivers synchronize the transition edge of the start bit.
CAN does not have any master-slave relation. Every interface unit is given each priority order (Identifier) to prevent from competition on the signal lines. When more than two units would start to transfer at the same time and they output their Identifiers after their start bits, each unit which receives a higher Identifier than its own immediately stops the data output. This guarantees that the data of the highest priority unit only can be transferred.
Lineup
Microcontrollers products incorporating a CAN interface are displayed.
Queries about purchasing, sampling and IC reliability
Stock Check & Purchase
require 3 characters or more.
Through this website you are able to proceed to the website of our distributors ("Third Party Website") which is not under the control of Toshiba Corporation and its subsidiaries and affiliates (collectively "Toshiba"). The Third Party Website is made available to you as a convenience only and you agree to use the Third Party Website at your own risk. The link of the Third Party Website does not necessarily imply a recommendation or an endorsement by Toshiba of the Third Party Website. Please be aware that Toshiba is not responsible for any transaction done through the Third Party Website, and such transactions shall be subject to terms and conditions which may be provided in the Third Party Website.

