- General Top View
-
SEMICONDUCTOR View
-
ApplicationsAutomotive
Body Electronics
xEV
In-Vehicle Infotainment
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Chassis
IndustrialInfrastructure
BEMS/HEMS
Factory Automation
Commercial Equipment
Consumer/PersonalIoT Equipment
Healthcare
Wearable Device
Mobile
Computer Peripherals
-
Products
Products
-
Design & Development
-
Knowledge
Knowledge
- Where To Buy View
-
- STORAGE View
- COMPANY View
- Part Number Search
- Cross Reference Search
- Keyword Search
- Parametric Search
- Stock Check & Purchase
This webpage doesn't work with Internet Explorer. Please use the latest version of Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox or Safari.
require 3 characters or more.
The information presented in this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's selection criteria and should be treated as a suggestion only. Please carefully review the latest versions of all relevant information on the TOSHIBA products, including without limitation data sheets and validate all operating parameters of the TOSHIBA products to ensure that the suggested TOSHIBA products are truly compatible with your design and application.
Please note that this cross reference is based on TOSHIBA's estimate of compatibility with other manufacturers' products, based on other manufacturers' published data, at the time the data was collected.
TOSHIBA is not responsible for any incorrect or incomplete information. Information is subject to change at any time without notice.
require 3 characters or more.
What drives transistors: current or voltage?
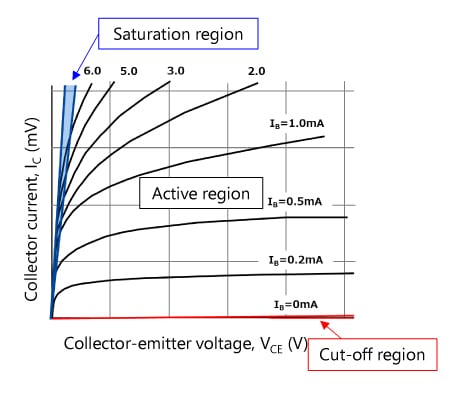
Basically, a bipolar transistor amplifies a small current entering the base to produce a large collector current. It is a current-driven device since the collector current is controlled via the base current. The current gain varies with the collector-emitter voltage (VCE). In the active region shown in the right-hand figure, a bipolar transistor provides a gain called a DC current gain (hFE) . In this region, the collector current remains almost constant regardless of the collector-emitter voltage (VCE). On the other hand, in the saturation region, a bipolar transistor exhibits a DC current gain of only 10 to 20, where the collector current considerably varies with VCE.
A field-effect transistor (FET) controls the width of a current path called the channel that is created by the voltage applied across the gate and source terminals. Changes in the channel width causes the drain-source resistance to change. Therefore, an FET is a voltage-driven device.
An IGBT is a device that combines a MOSFET, a type of FET, in the front stage and a bipolar transistor in the rear stage. An IGBT operates in the same manner as an FET when it turns on. Therefore, an IGBT is also a voltage-driven device.
Chapter 3, “Transistors,” of the e-learning session provides related information.

